Cellular Respiration In Plants Equation

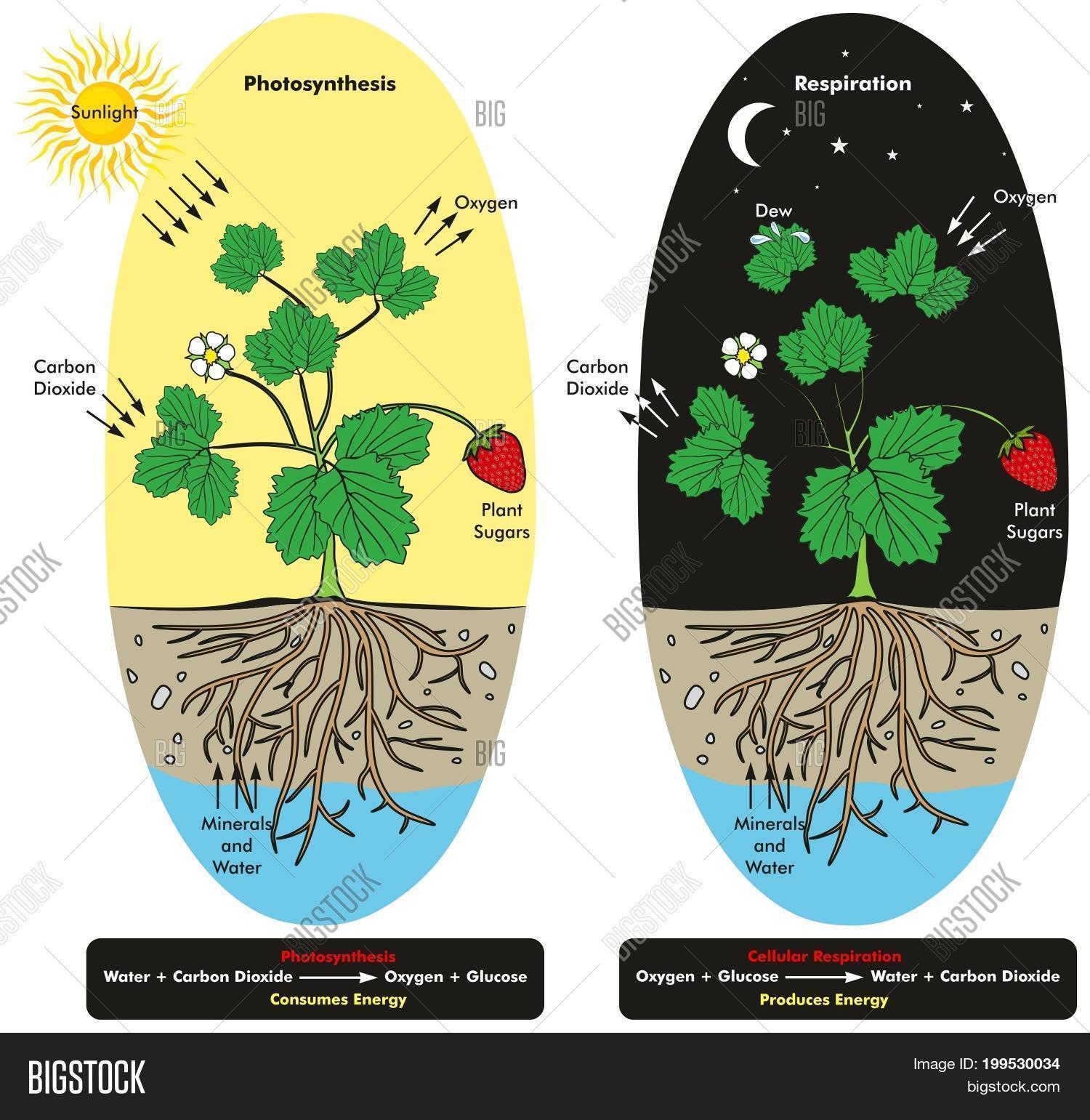
Special cells in the leaves of plants called guard cells open and close the stomata.
Cellular respiration in plants equation. The cellular respiration equation is a part of metabolic pathway that breaks down complex carbohydrates. It involves the splitting of pyruvic acid produced by glycolysis into carbon dioxide and water along with the production of adenosine triphosphate ATP molecules. Name the respiratory organ in woody stems.
In hard and woody stems respiration or the exchange of gases takes place through lenticels. Cellular Respiration In Plants Equation. Cellular Respiration Ck 12 Foundation.
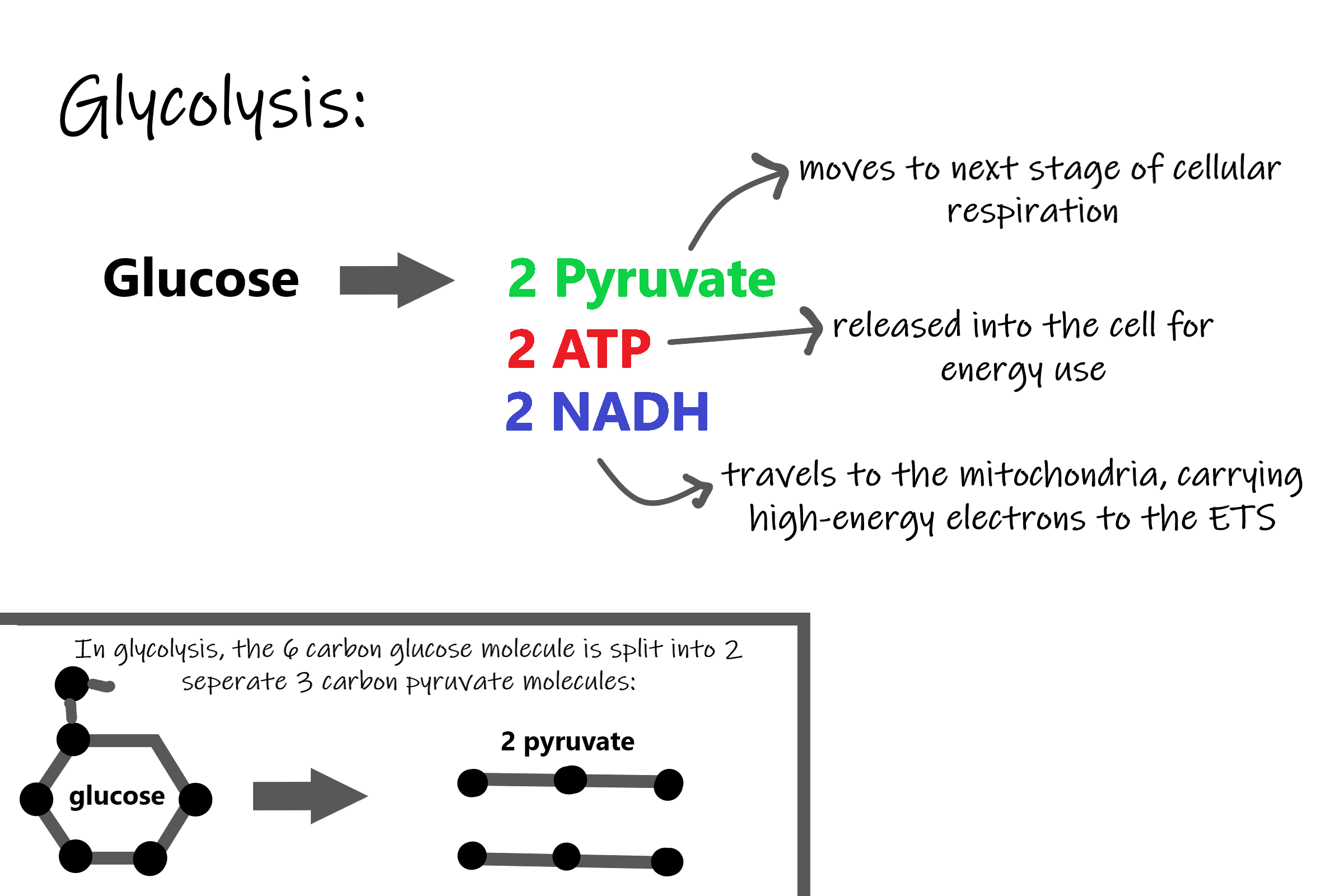
Thus the net gain of ATP during glycolysis is 4 2 2 ATP. Cellular respiration involves many chemical reactions but they can all be summed up with this chemical equation. Glucose oxygen carbon.
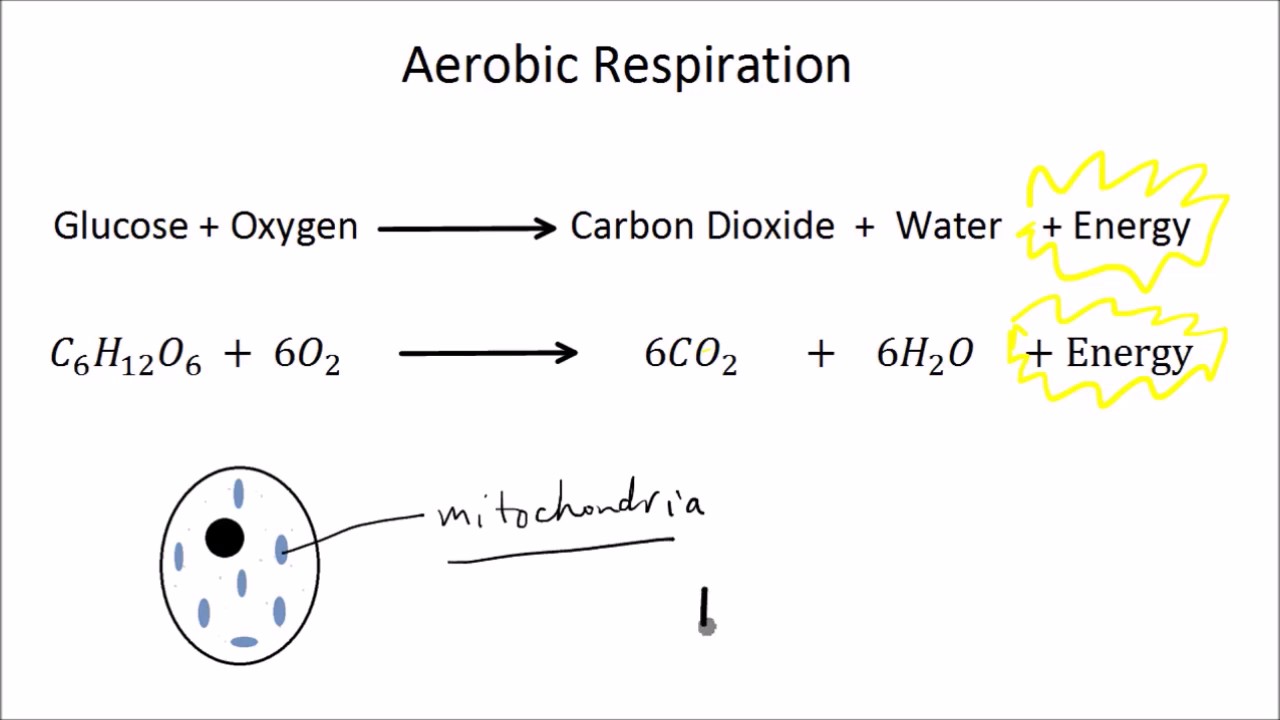
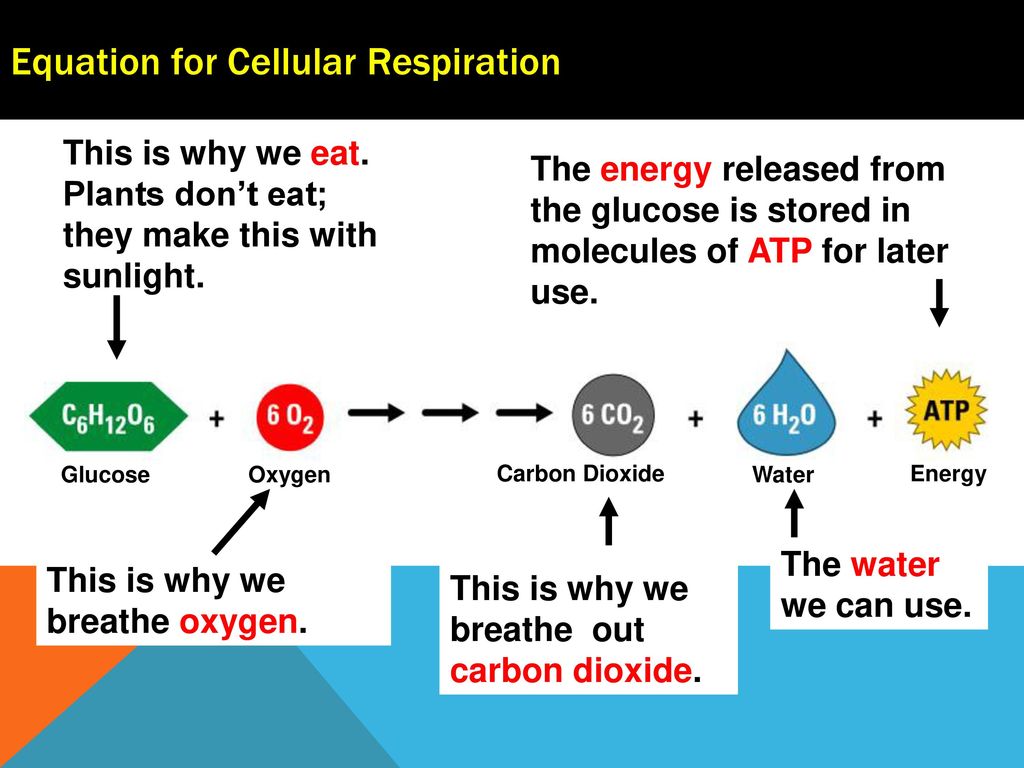
Understanding Cellular Respiration Here are three visual depictions of cellular respiration an equation an output description and an illustration. This process yields a lot of ATP for the plant to use for growth and reproduction. The balanced chemical equation for this reaction is c6h1206 6o2 6co2 6h2o energy atp.
Meanwhile carbon dioxide is formed and electrons are removed and placed into an electron transport system. C 6 H 12 O 6 6 O 2 6 CO 2 6 H 2 O 38 ATP In this formula C 6 H 12 O 6 is glucose or sugar. The reason the 6 is put in front of carbon dioxide is to balance out.
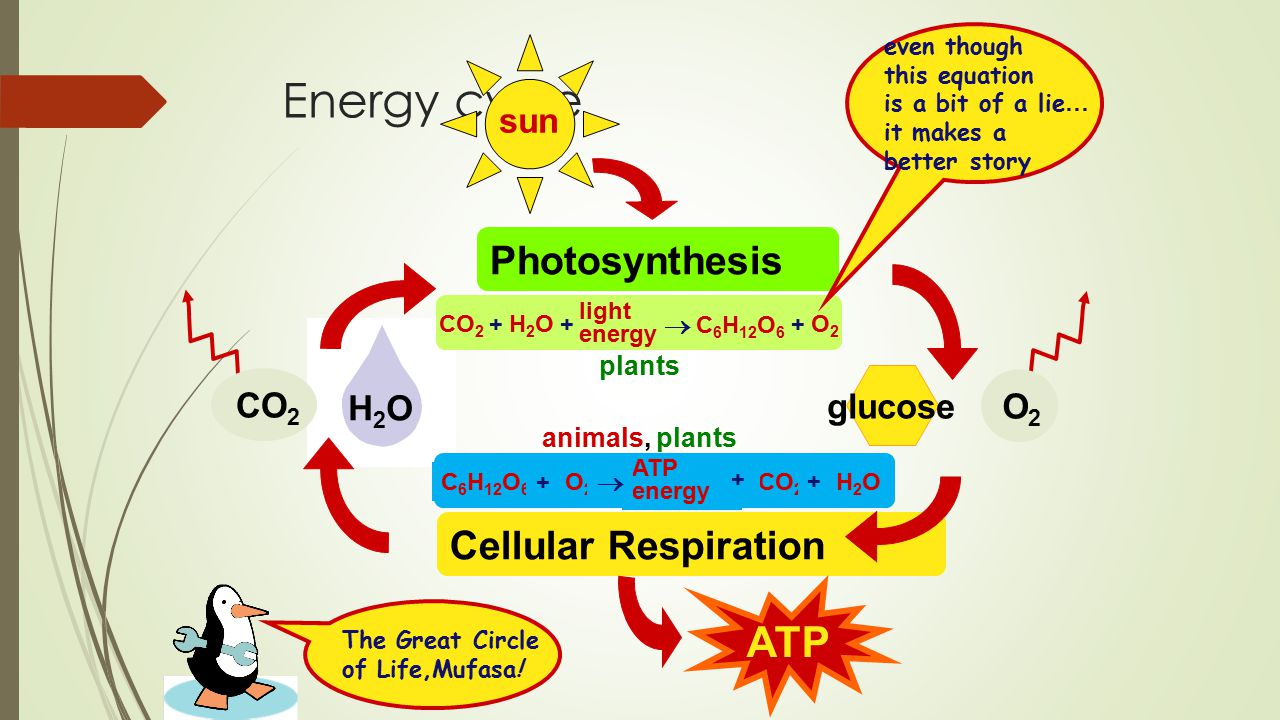
The glucose is then used by the plants or organisms that consume the plants for the process of cellular respiration to make atp. The equation for photosynthesis is the inverse of the equation for cellular respiration. Cellular respiration aerobic c6h12o6 6o2 6co2 6h2o 32 atp.