Food Chain Definition Ecology

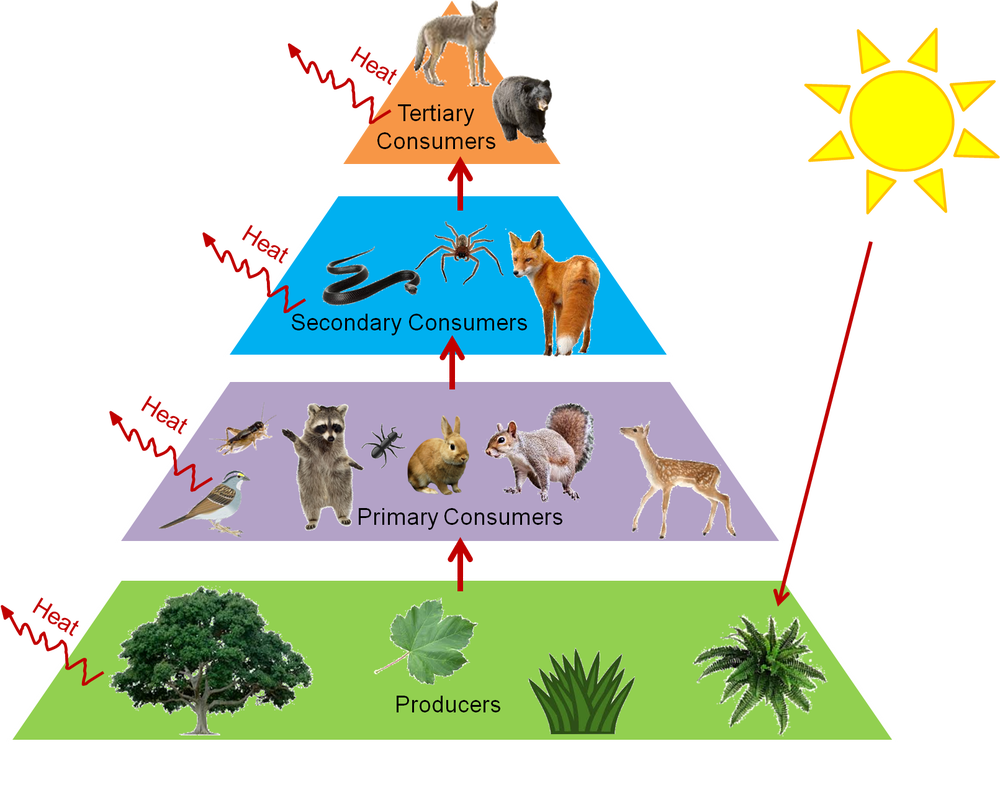
In a community which has producers consumers and decomposers the energy flows in a specific pathway.
Food chain definition ecology. Find the Food Chain Definition Ecology including hundreds of ways to cook meals to eat. Food chain - ecology a community of organisms where each member is eaten in turn by another member bionomics environmental science ecology - the branch of biology concerned with the relations between organisms and their environment. This occurs when one organism consumes another organism.
The idea to apply the food chains to ecology and to analyze its consequences was first proposed by Charles Elton Krebs 2009. Every living thingfrom one-celled algae to giant blue whale sneeds food to survive. The food chain is a linear sequence of organisms where nutrients and energy are transferred from one organism to another.
English 1775114 1977 briefly itemized the stages of two food chains one terrestrial one aquatic Egerton 2007a. Video about Food Chain Definition Ecology. It begins with producer organism follows the chain and ends with decomposer organism.
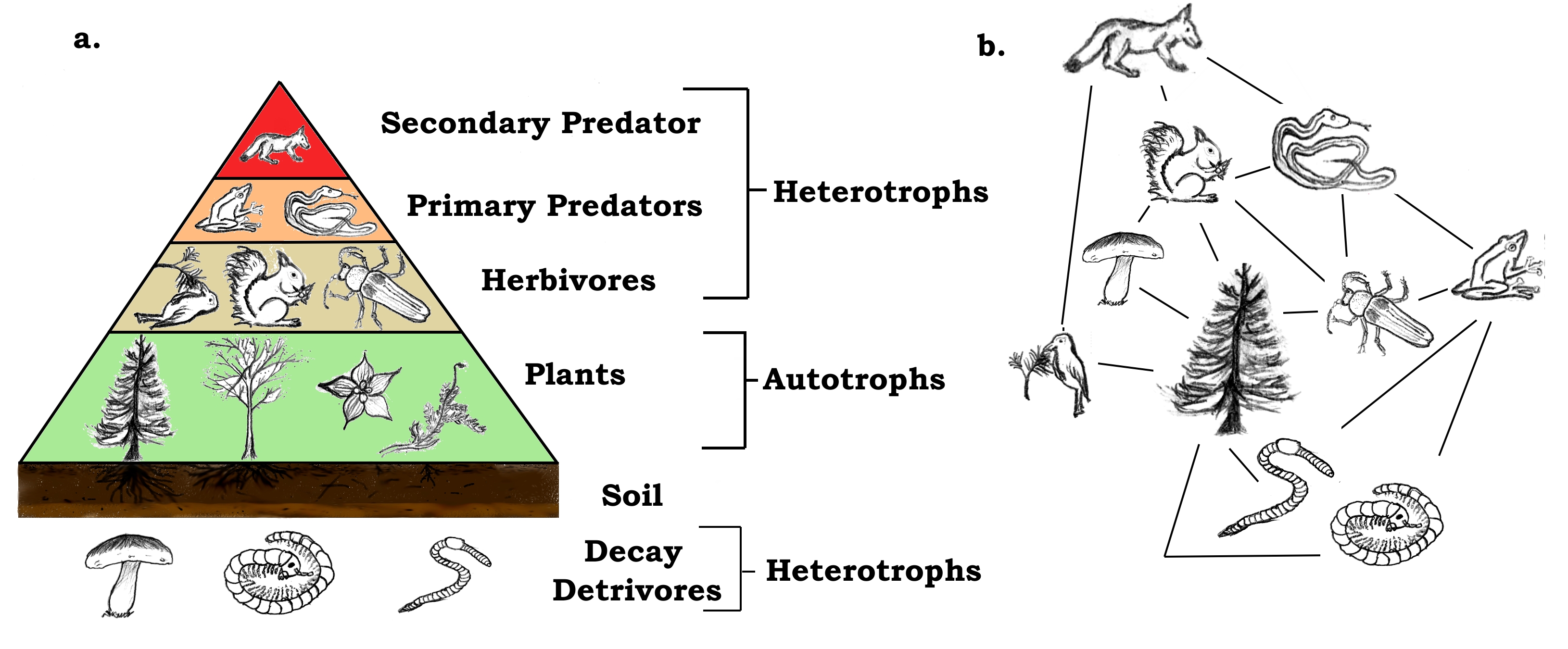
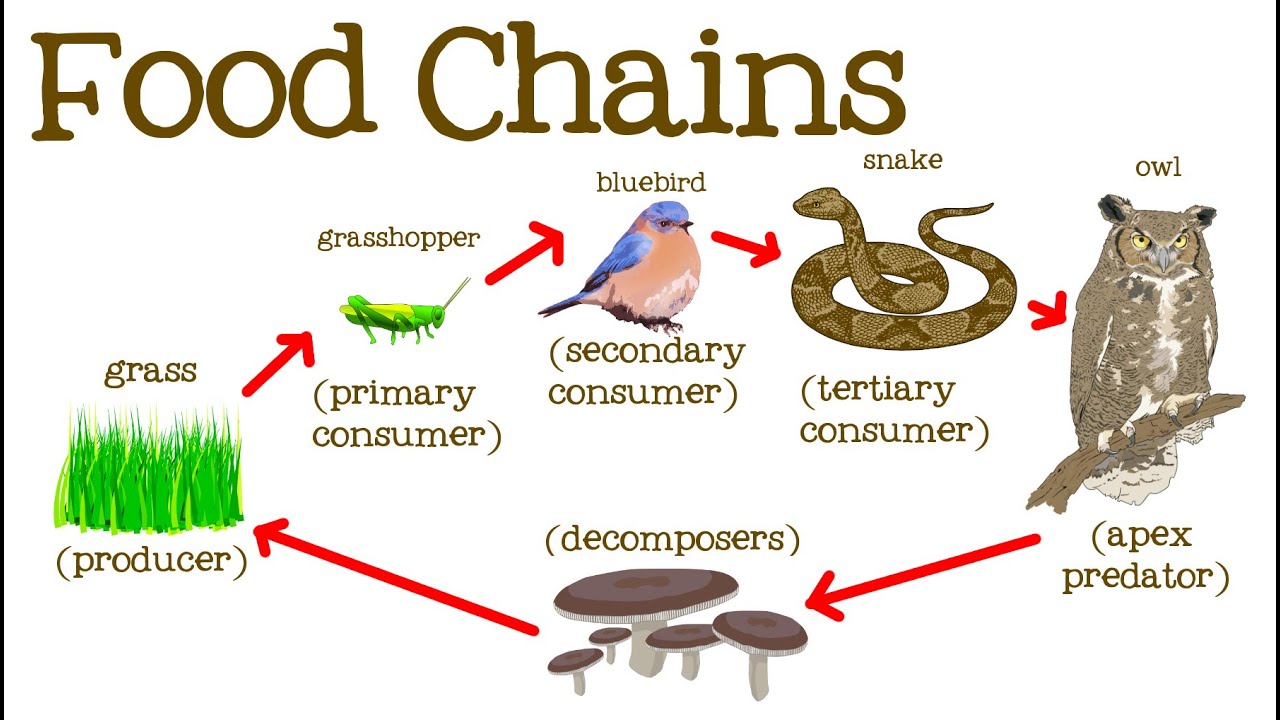
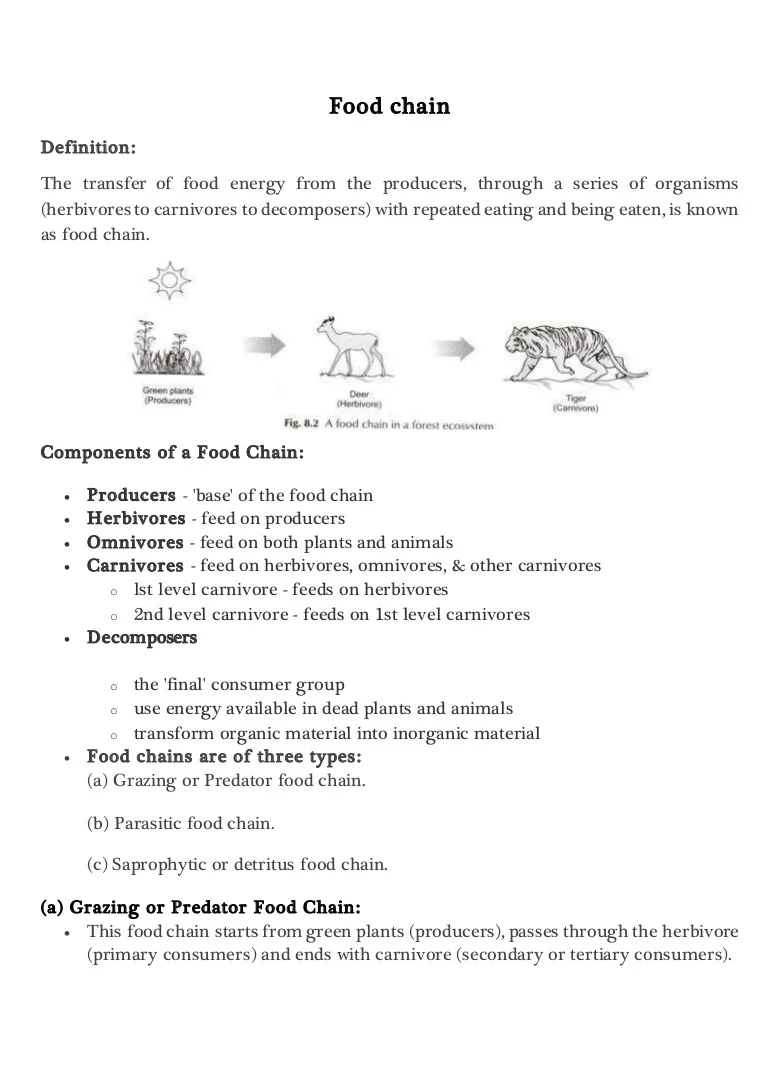
A food chain in a grassland ecosystem may consist of grasses and other plants grasshoppers frogs snakes and hawks figure 83. In ecology a food chain is a series of organisms that eat one another so that energy and nutrients flow from one to the next. The producers in a food chain include all green plants.
Food chain definition ecology. Food ecology is the science which looks at the food production process and assesses the impact each stage of the process has on how plants and animals relate. The term food chain describes the order in which organisms or living things depend on each other for food.
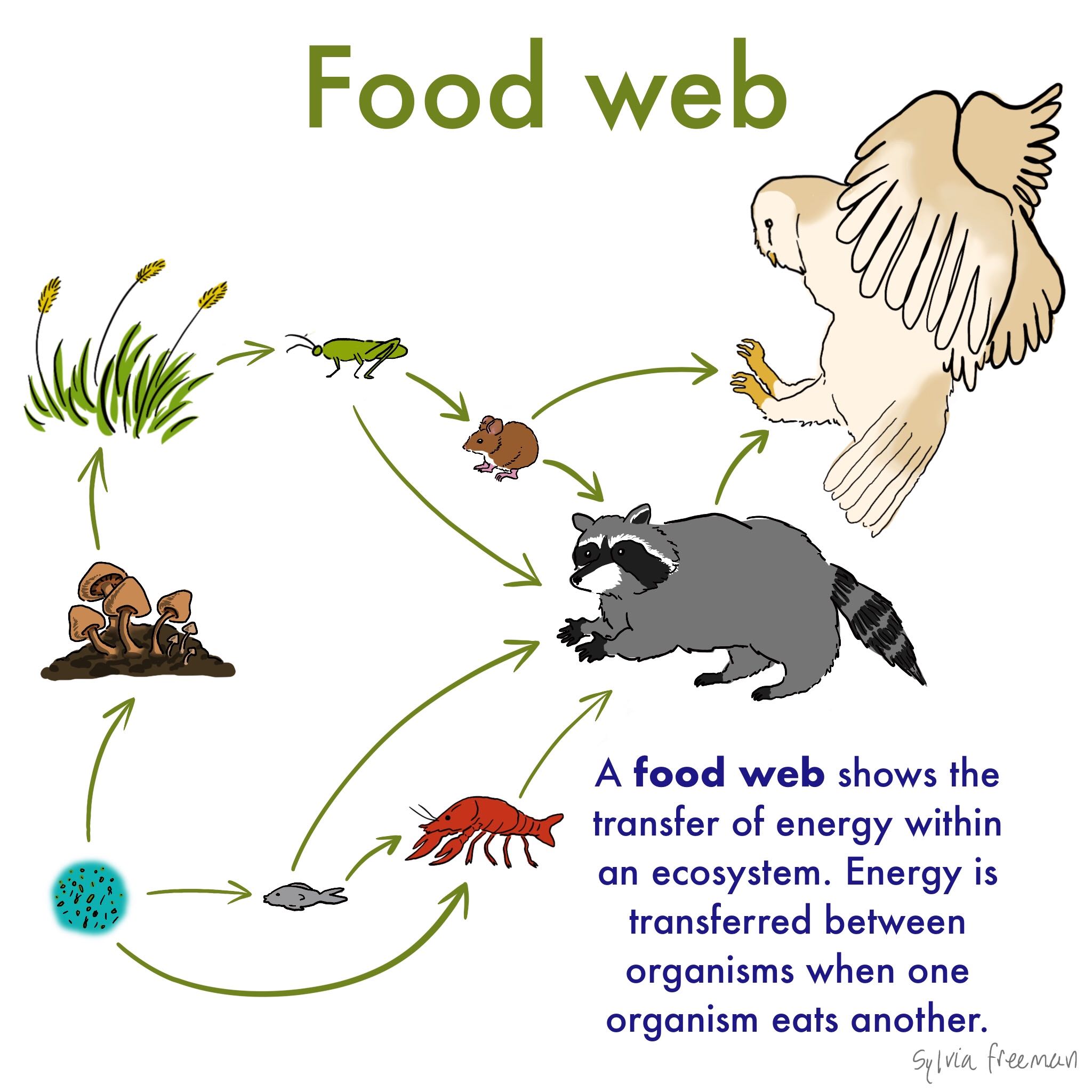
From the examples given above we can understand that how the food material forms consumers of different levels of the food chain based on producers. Food chains intertwine locally into a food web because most organisms consume more than one type of animal or plant. In 1927 he recognized that the length of these food chains was.